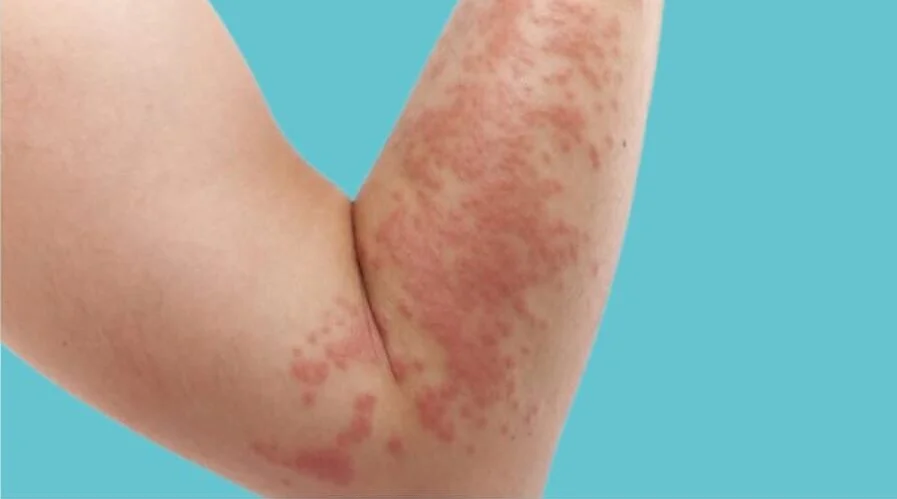
Hives (urticaria) is a skin condition characterized by a rash, which can be caused by allergic reactions, medical conditions, or other triggers. Acute hives develop quickly and typically resolve within six weeks, whereas chronic hives can persist for months or even years. Identifying specific triggers, such as certain foods, medications, or stress, can help manage the condition, but in many cases, the cause remains unclear. If hives significantly impact quality of life or do not resolve, consulting a doctor is recommended. In rare cases, hives accompanied by symptoms like swelling in the mouth or throat, nausea, faintness, rapid heartbeat, or cold skin may indicate anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Proper diagnosis and treatment can provide relief and prevent complications.
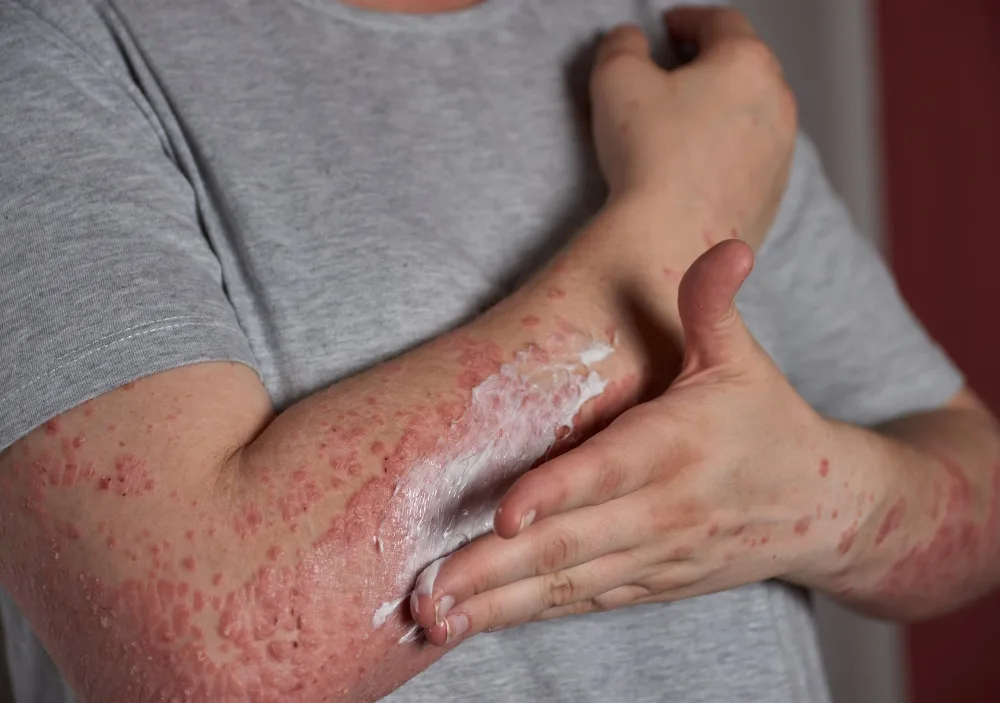
Treatment for hives, typically involves the use of oral medicines, which help relieve itching and reduce swelling by blocking triggered by an allergen. The challenge in treating hives lies in identifying the exact allergen or trigger, which can vary from foods, medications, insect stings, stress, or infections. Sometimes, the cause remains unknown. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding known triggers, can be an important part of managing the condition. In persistent or chronic cases, other treatments such as immune-modulating drugs may be recommended. Understanding the root cause of hives is crucial for effective treatment and long-term relief.
A1: Yes, most cases of hives can be treated with antihistamines, soothing creams, or other medications, depending on the severity.
A2: Yes, many cases of acute hives resolve on their own within hours or days, especially if the trigger is identified and avoided.
A3: No, hives are not contagious. They are typically caused by an allergic reaction, physical triggers, or underlying conditions.
A4: Yes, identifying and avoiding triggers such as specific foods, medications, or environmental factors can help prevent hives from occurring.
A5: Yes, soothing baths, cold compresses, and over-the-counter antihistamines can help relieve the itching and discomfort of hives.
A6: Yes, stress can be a trigger for hives, so practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga can help prevent flare-ups.
A7: Yes, children can get hives, especially in response to insect bites, certain foods, or viral infections, but most cases resolve with time.
A8: Yes, chronic hives can often be managed with medications like antihistamines or injectable treatments, and the symptoms can improve over time.
A9: While there is no definitive cure for chronic hives, many people can manage the condition effectively with the right treatment plan.
A10: If hives continue or are accompanied by severe symptoms such as trouble breathing, it is crucial to seek medical attention. However, most cases can be managed at home with appropriate care
Klarity Skin Clinic, M – 69, First Floor,
M Block Market, Greater Kailash II, New Delhi 110048
Copyright © 2025 All Rights Reserved.
Klarity Skin Clinic is Unit of Acara Wellness Private Limited.