Hives (urticaria) is a skin condition characterized by a rash, which can be caused by allergic reactions, medical conditions, or other triggers. Acute hives develop quickly and typically resolve within six weeks, whereas chronic hives can persist for months or even years. Identifying specific triggers, such as certain foods, medications, or stress, can help manage the condition, but in many cases, the cause remains unclear. If hives significantly impact quality of life or do not resolve, consulting a doctor is recommended. In rare cases, hives accompanied by symptoms like swelling in the mouth or throat, nausea, faintness, rapid heartbeat, or cold skin may indicate anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Proper diagnosis and treatment can provide relief and prevent complications.
Hives
Talk to Experts
Stop the Itch: Proven Treatments for Hives
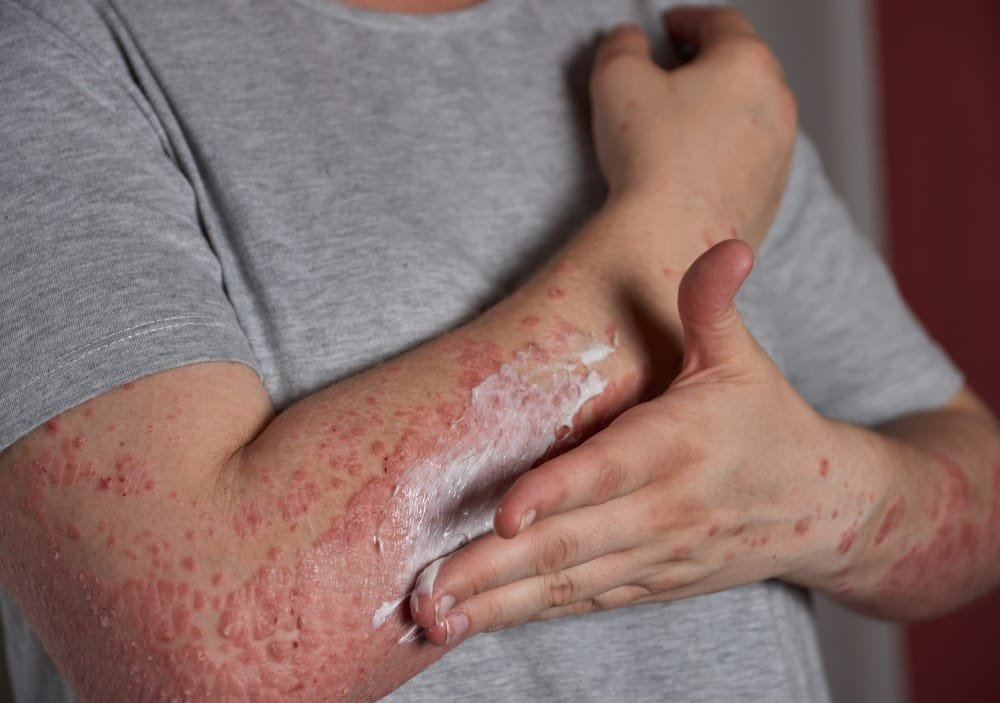
Treatment Benefits
- Reduces itchiness
- Clears skin welts
- Relieves angioedema
- Minimizes inflammation
- Eases allergic reactions
- Promotes skin comfort
- Reduces swelling
- Quick symptom relief
- Prevents recurrence
Symptoms and Treatment for Hives
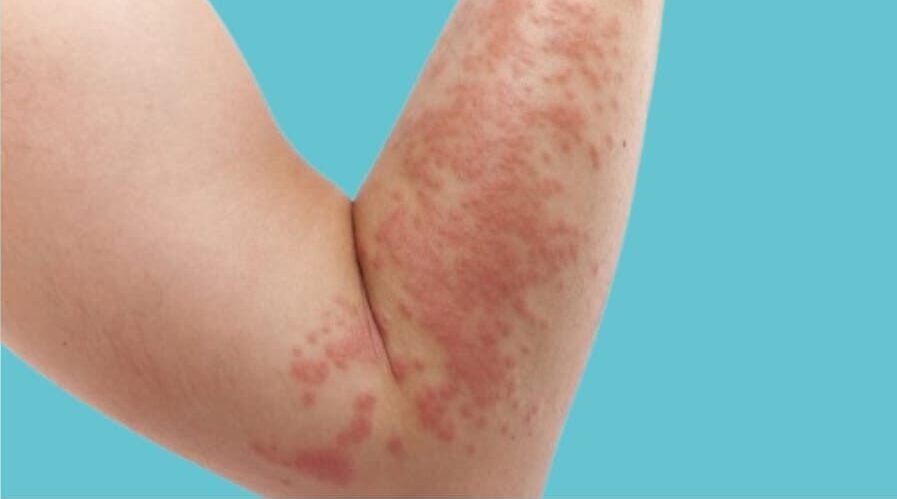
Symptoms and Treatment for Hives
Treatment for hives, typically involves the use of oral medicines, which help relieve itching and reduce swelling by blocking triggered by an allergen. The challenge in treating hives lies in identifying the exact allergen or trigger, which can vary from foods, medications, insect stings, stress, or infections. Sometimes, the cause remains unknown. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding known triggers, can be an important part of managing the condition. In persistent or chronic cases, other treatments such as immune-modulating drugs may be recommended. Understanding the root cause of hives is crucial for effective treatment and long-term relief.
Symptoms
- Itchy bumps
- Red welts
- Raised patches
- Swollen skin
- Blister-like lesions
- Skin redness
- Burning sensation
- Rash outbreaks
- Tingling sensation
