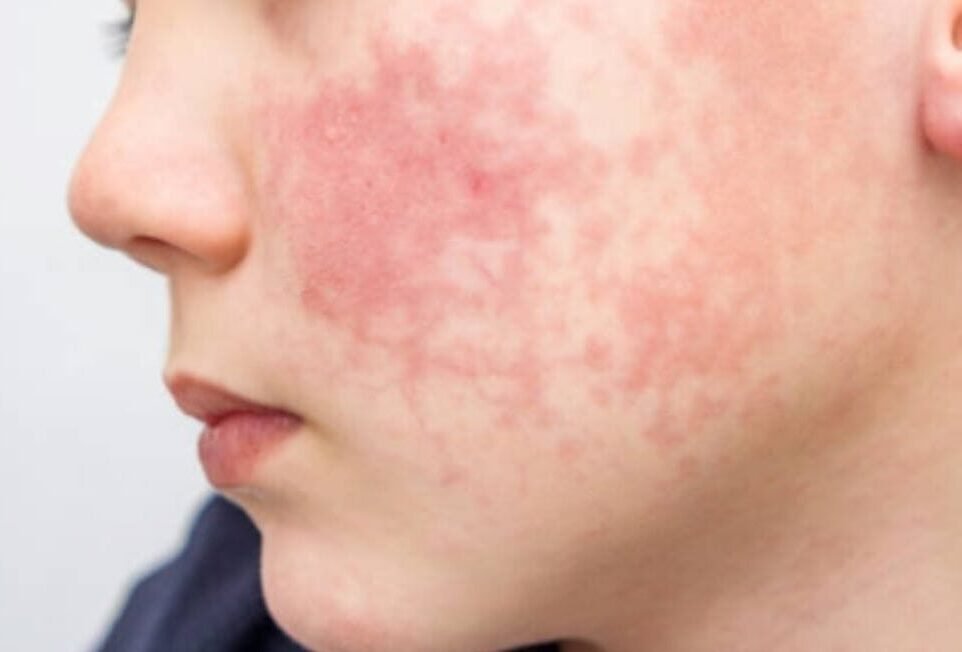
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition causing dry, itchy, and inflamed patches. It typically begins in childhood, often within the first six months. While atopic dermatitis is common, it can be severe and long-lasting. It usually improves as a child grows older, though flare-ups may persist into adulthood. The condition weakens the skin’s barrier, making it harder to retain moisture and protect against irritants. Eczema is not contagious but results from genetics, environmental triggers, and conditions like asthma, hay fever, or allergies. Types of eczema include atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, nummular eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis, with some individuals experiencing multiple types.
Eczema / Atopic Dermatitis
Talk to Experts
Eczema : Causes and Types
Treatment Benefits
- Reduces Inflammation
- Relieves Itching
- Calms Skin Irritation
- Improves Skin Texture
- Restores Moisture
- Reduces Flare-Ups
- Boosts Skin Elasticity
- Promotes Healing
- Minimizes Redness
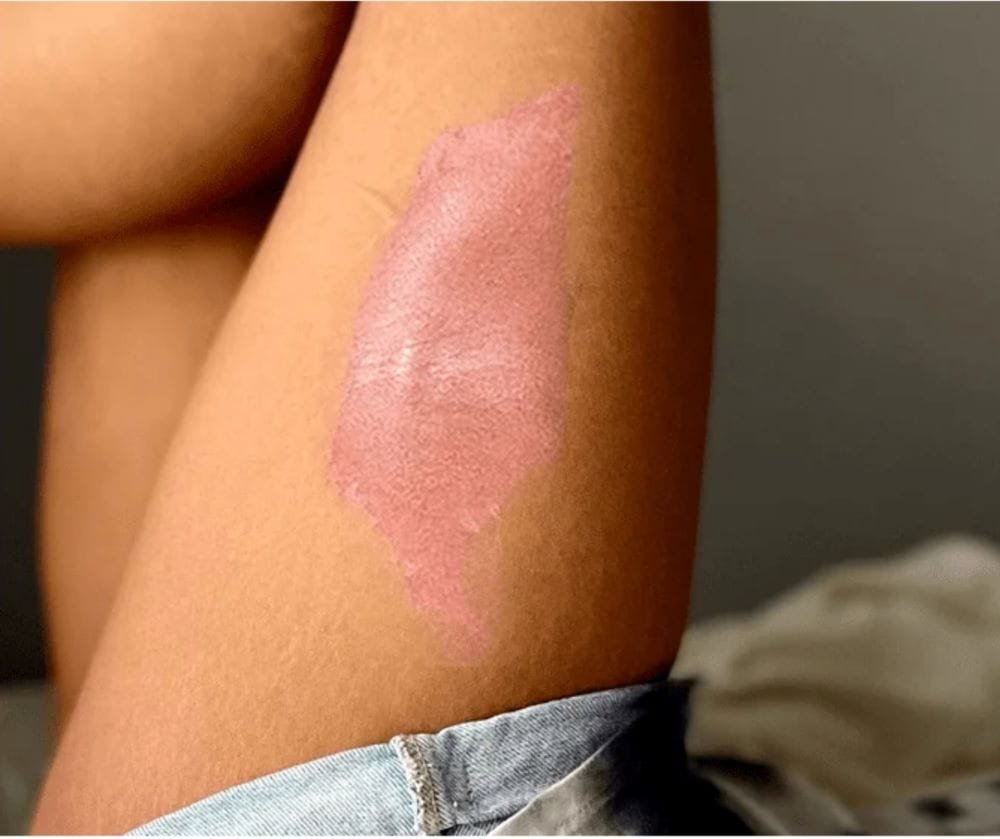
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) : Symptoms and Treatment
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis) : Symptoms and Treatment
Treatment for eczema aims to reduce inflammation and ease symptoms. This includes topical treatments to calm inflammation, moisturizers to restore hydration, and antihistamines to manage itching. Additionally, lifestyle modifications to avoid known triggers and irritants are key to controlling flare-ups. Managing stress, using gentle skincare routines, and staying hydrated also help maintain long-term symptom control. Avoiding harsh soaps, extreme temperatures, and allergens can minimize flare-ups. Regular use of prescribed treatments and adjustments to daily habits can improve skin health and comfort over time.
Symptoms of Eczema
- Itchy skin
- Red patches
- Dry skin
- Inflamed areas
- Flaky skin
- Cracked skin
- Blister-like sores
- Thickened skin
- Scaly patches
