Fungal infection
Talk to Experts
Fungi are living organisms classified separately from plants and animals. They reproduce by releasing spores into the air or surrounding environment. Many fungi naturally reside in the body, such as in the mouth, GI tract, and on the skin, but they can overgrow under certain conditions. Only a small number of fungi, like specific yeasts and moulds, cause diseases in humans. Fungal infections can cause symptoms like red, swollen, bumpy skin, discoloured or thick nails, and white patches in the mouth or throat. Anyone can get a fungal infection, but those with poor circulation, diabetes, or a weakened immune system are at higher risk. Proper hygiene and treatment are key to managing fungal infections and preventing their spread.
Fight Fungal Infections Effectively
Treatment Benefits
- Relief from itching
- Clears scaly skin
- Broad-spectrum solutions
- Strengthens immunity
- Eliminates infection source
- Easy topical treatments
- Oral medication options
- Prevents recurrence
- Enhanced skin health
Fungal Infections: Types, Causes and Solutions
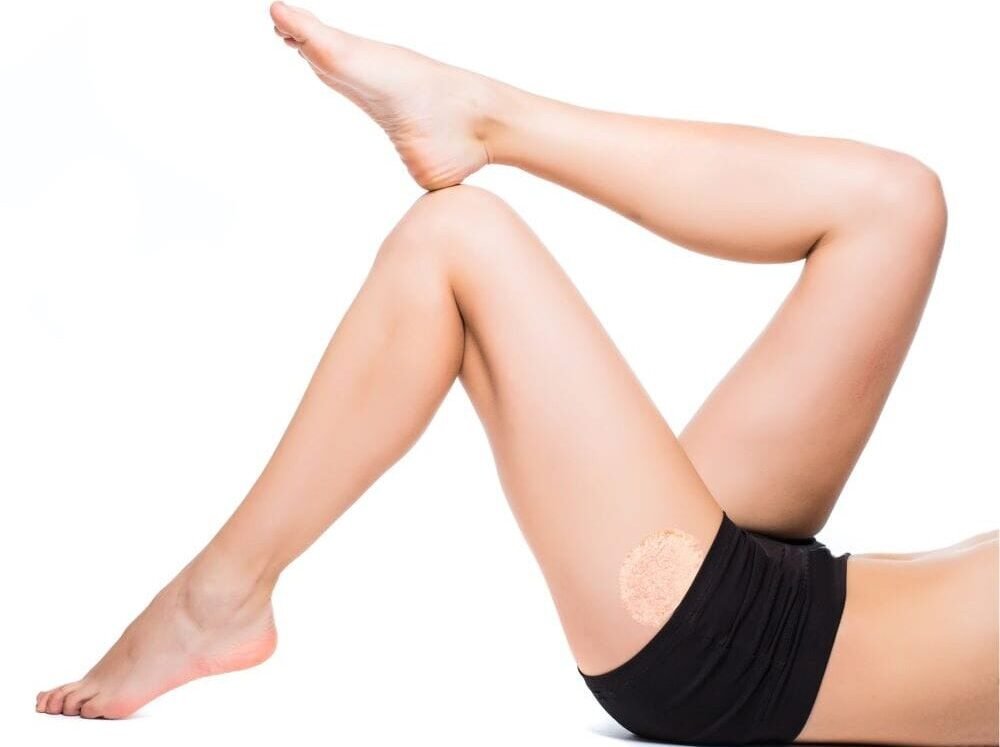

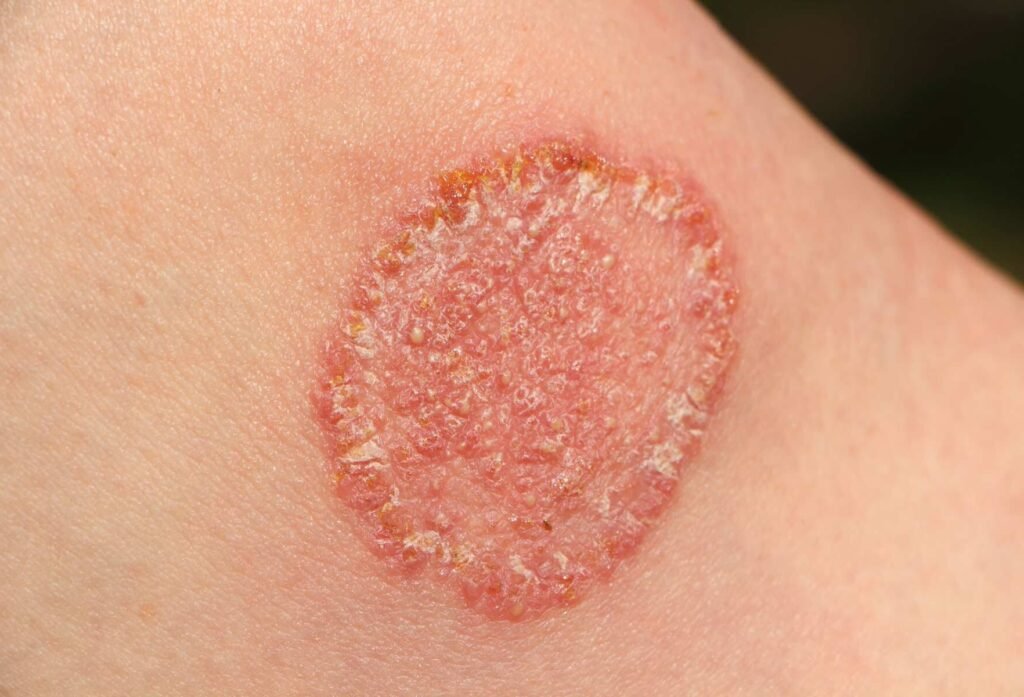
Fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections, cause symptoms like scaly skin, redness, itching, swelling, and thickened or discoloured nails. These infections often develop in areas prone to moisture and friction, like between toes, groin, or underarms. People with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or poor circulation are more prone to severe infections. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, such as topical creams, oral meds, or antifungal shampoos, depending on the infection type. Proper hygiene, keeping areas dry, and following prescribed treatments can prevent recurrence, manage symptoms, and promote healing. Timely treatment is essential to avoid complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection.
Fungal Infections Symptoms
- Itchy skin
- Red patches
- Swollen skin
- Bumpy texture
- Thickened nails
- Discolored nails
- Cracked skin
- White patches
- Blister-like sores
